Energy isn’t all created equal. And as daily energy users, we all have a responsibility to understand where our energy comes from and how it affects the environment. Thankfully, we now can determine where our energy comes from and, in many situations, select where it comes from.
Let’s start with a definition of green energy solutions, and then we’ll go into its advantages and other aspects.
What Is Green Energy?
Natural sources of green energy include sunlight, rain, wind, plants, algae, tides, and geothermal heat. These energy supplies are renewable, which means they can be renewed naturally. On the other hand, fossil fuels are a limited resource that took millions of years to generate and will continue to deplete as they are used.
On the other hand, green energy makes use of easily accessible energy sources all over the globe, particularly in rural and distant locations where power is unavailable. Green energy may be used to replace fossil fuels in various applications, including electricity, water heating, household appliances, and automobile fuel.
The Benefits of Green Energy
There are several benefits of green energy investing, including lowering carbon emissions, averting additional environmental damage, and generating employment. As a result, by purchasing green energy, you contribute to the advancement of that future.
With enough solar power to power the whole world daily, there’s one problem: There’s not enough of it. Current methods are insufficiently efficient to convert enough of it into energy, and for many, it is more cost-effective to rely on other conventional sources.
Going green entails increased investment in solar, wind, and other such renewable energy projects and the development of technology that better utilizes the renewable resources available to us and makes them more cheap and accessible to everyone.
Types of Green Energy
The most common energy sources are wind, solar, and hydroelectric electricity. It is possible to generate solar and wind power on a limited scale at home or on a larger scale in an industrial setup. The following are some of the most common types:
1. Solar Power
Green energy sources such as photovoltaic cells, which turn sunlight into power, are widely used. Buildings are heated, hot water is provided, food is cooked, and light is provided using solar energy. Solar energy has become affordable enough for domestic applications like garden lighting and entire power towns on a larger scale.
Read More: About the Solar Energy
2. Wind Power
Wind turbines may be propelled by airflow on the earth’s surface, with stronger winds yielding more energy. The ideal circumstances for catching the strongest winds are at high altitudes and near offshore. A network of 2.5-megawatt land-based wind turbines in rural regions with 20% of their rated capacity may provide 40 times the present global energy demand.
Read More: About the Wind Energy
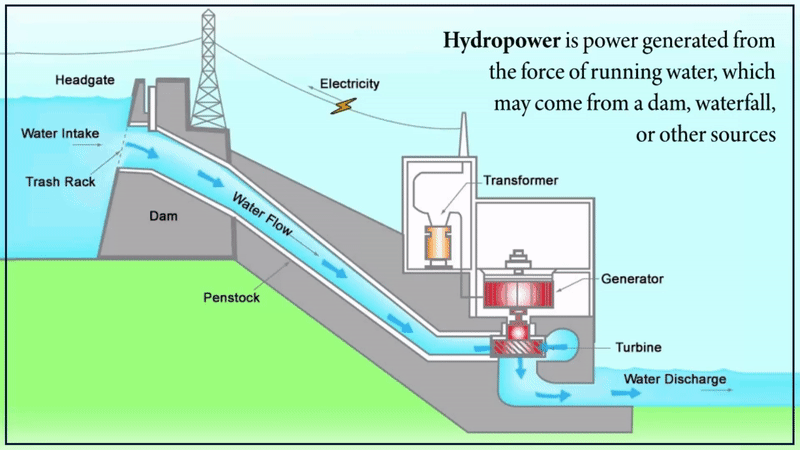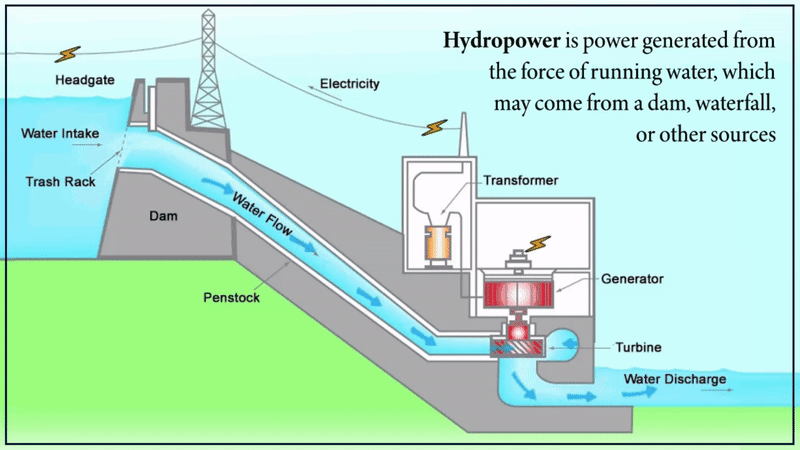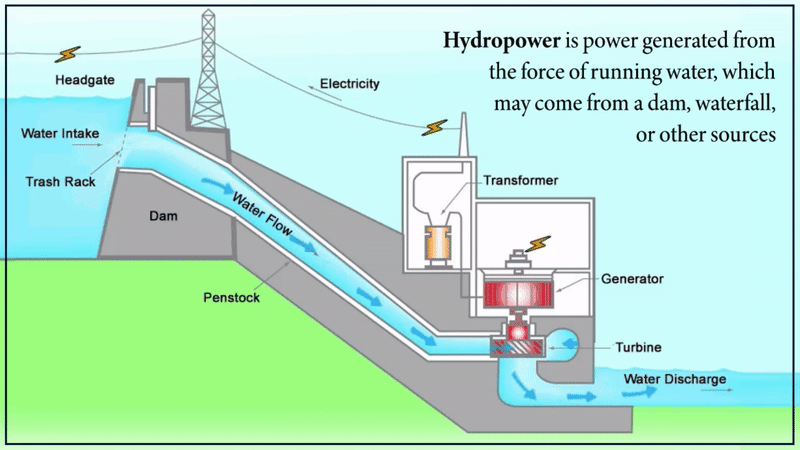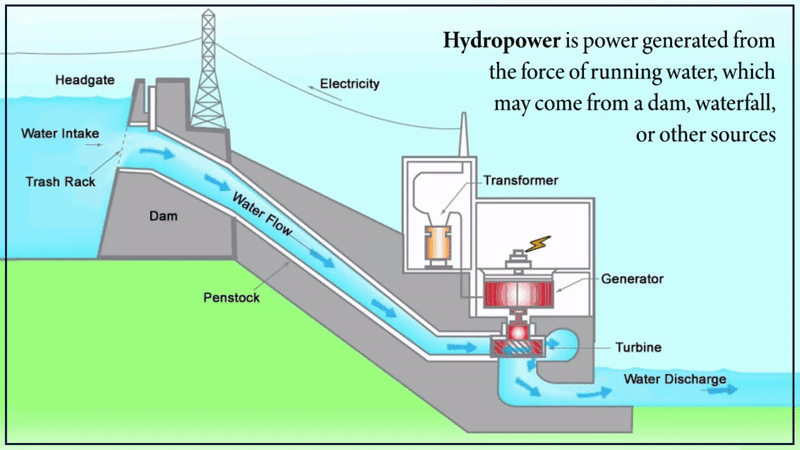
3. Hydropower
This sort of green energy, also referred to as hydroelectric power, generates electricity by harnessing the power of flowing water in rivers, dams, streams, and other bodies of water. Hydropower may be generated on a small scale, for example, by the flow of water via pipes in the house, or it can be generated by absorption, rainfall, or even the tides in the seas.
Read More: About the Hydropower
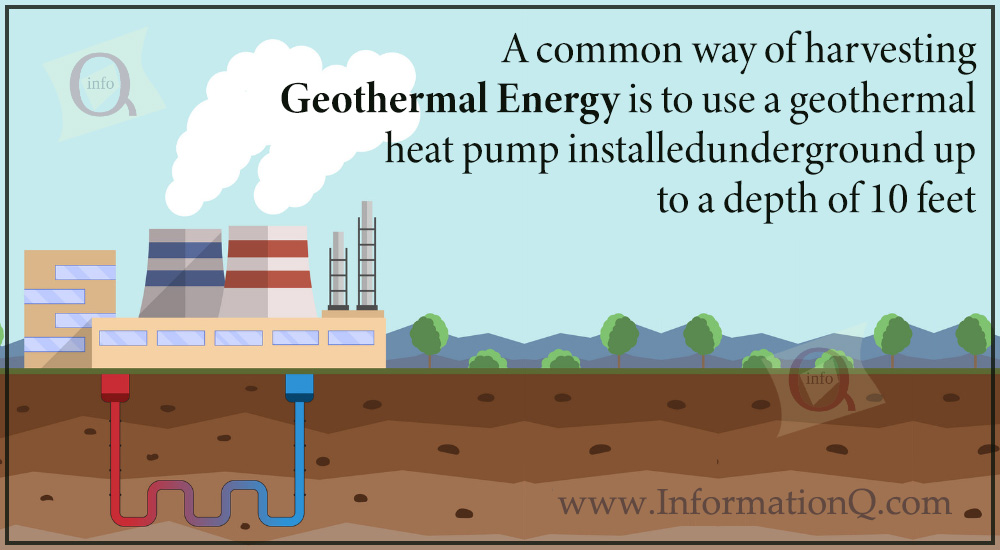
4. Geothermal Energy
Earth’s crust contains vast quantities of thermal energy that stem from both the planet’s genesis and radioactive decay. Humans have utilized geothermal energy in the form of hot streams for thousands of years to heat water for bathing. Now geothermal energy in hydroelectric dams is being used to create electricity.
Read More: About the Geothermal Energy
5. Biomass Energy
This renewable resource must be managed appropriately to qualify as a “green energy” source. Waste biomass such as wood chips or sawdust may be used to create electricity and organic agricultural waste. While these materials release greenhouse emissions, they are substantially lower than those generated by petroleum-based fuels.
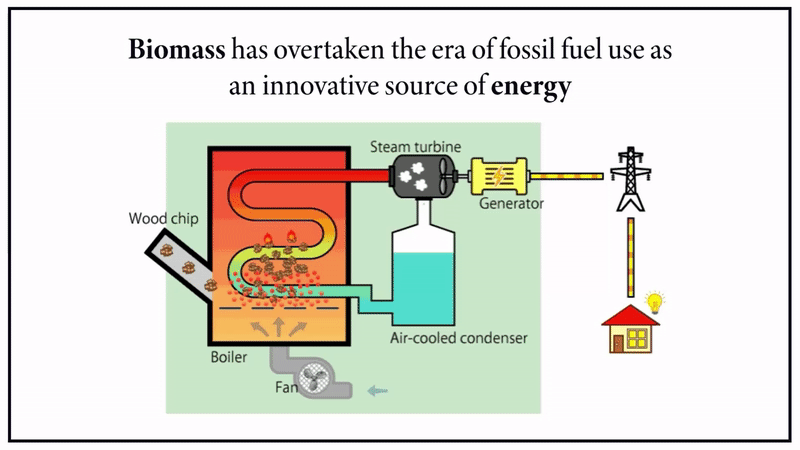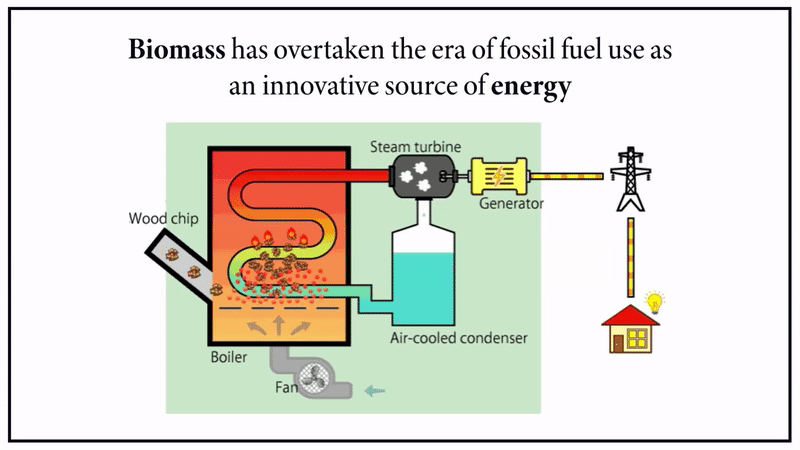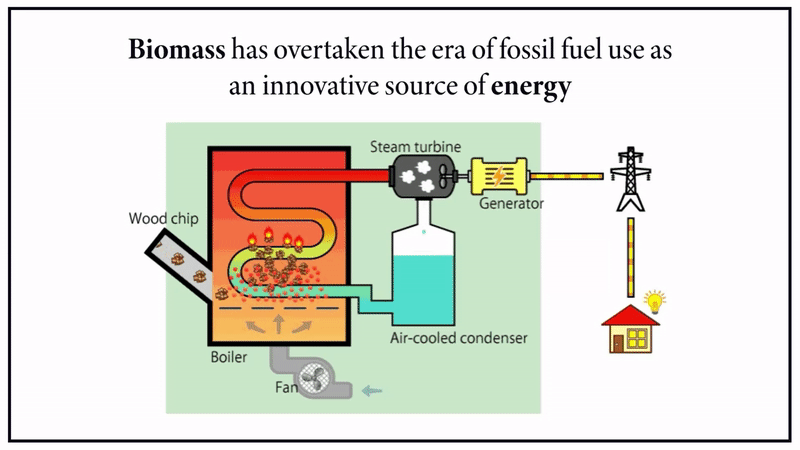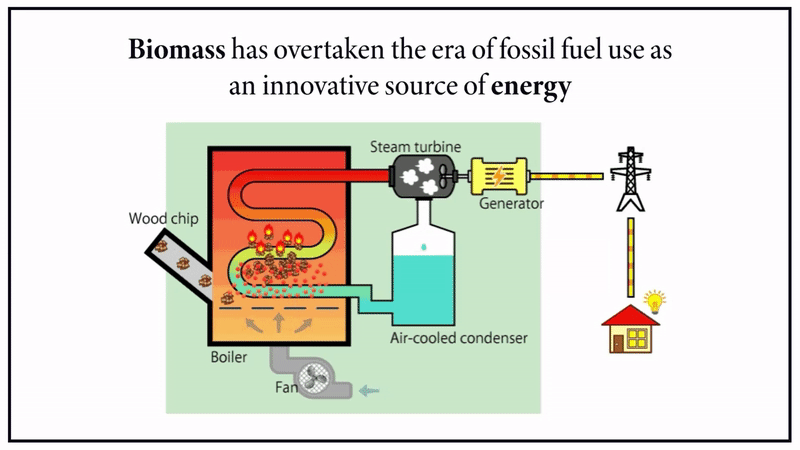


Read More: About the Biomass Energy
6. Biogas Energy
It is possible that biogas if it exists, is both a renewable energy source and a method of converting waste into energy. Organic matter decomposes to produce biogas, which may be found in sewage, food waste, and manure from farms. Without oxygen in the containers, these compounds ferment and create gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
Read More: About the Biogas Energy
What Is the Importance of Green Energy?
To power our houses in the past, we relied on fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and kerosene. On the other hand, these fuels are non-renewable and harm our environment and climate. Consequently, these resources will eventually run out, causing shortages and scarcity.
But what’s worse is the environmental harm they cause—the usage of traditional energy sources contributes to global warming. Poisonous gases are released into the atmosphere by coal and oil, damaging general health, causing respiratory difficulties, and decreasing life spans.
Oil and coal extraction alone may devastate an area’s ecology, economy, and lives by causing massive oil spills. There are several advantages of green energy, such as it may help us alleviate and even avoid some of these problems.
Read also this
Electrical Energy
Read more Who Invented Electricity?
Read more ‘Renewable Energy Sources’
In Conclusion
An eco-friendly alternative to many of the world’s current energy sources seems to be in the cards for the future. These energy sources, which are abundantly replenished, are excellent for the environment and employment generation, and they seem to be economically viable as time progresses.



Leave a Reply